Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM)
What is SLAM?
Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) is a computational problem of constructing or updating a map of an unknown environment while simultaneously keeping track of an agent's location within it. SLAM is commonly used in robotics and autonomous systems, where a robot needs to navigate and understand its surroundings without prior knowledge of the environment.
Key Components of SLAM:
- Localization: Estimating the robot's position in the environment.
- Mapping: Creating a map of the environment using sensor data.
- Sensor Fusion: Combining data from different sensors such as LIDAR, cameras, or IMUs to improve accuracy.
Applications of SLAM:
- Autonomous mobile robots
- Augmented reality
- Drones and autonomous vehicles
JarvisBot SLAM Packages
JarvisBot uses a set of SLAM-related packages to achieve accurate localization and mapping in real time. These packages handle sensor integration, algorithm processing, and data management for SLAM.
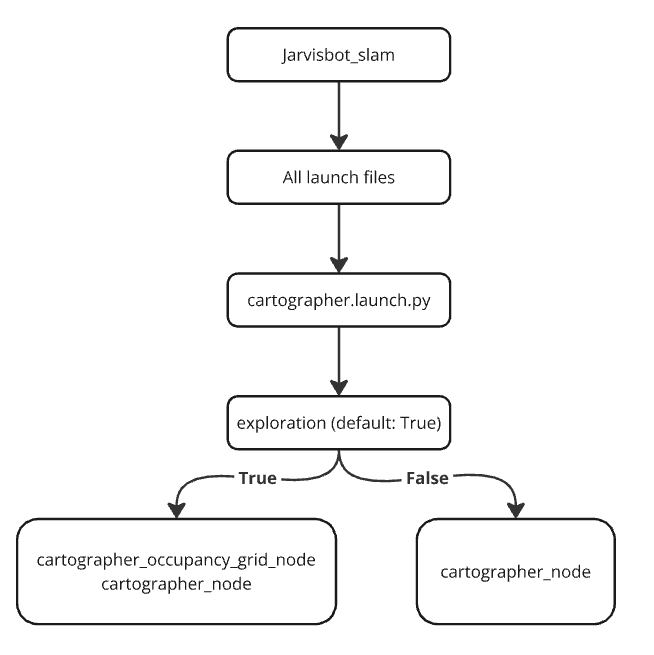
Key SLAM Packages in JarvisBot:
-
Sensor Drivers:
- These packages interface with the robot’s sensors (LIDAR, camera, IMU) and collect data for SLAM processing.
-
SLAM Algorithms:
- The core SLAM algorithms (like Extended Kalman Filter, Particle Filter, or Graph SLAM) that process sensor data and compute the map and robot position.
-
Mapping Package:
- Handles the construction of a 2D or 3D map of the environment by processing sensor data and aligning observations with previously built sections of the map.
-
Localization Package:
- Maintains the robot’s estimated position within the environment, often using particle filters or Monte Carlo methods.
Features:
- Real-time localization: Provides accurate robot positioning in dynamic environments.
- Sensor fusion: Integrates data from LIDAR, IMU, and other sensors for robust SLAM performance.
- Modular design: Easily extendable to support more sensors and algorithms as needed.
Usage
To run the cartographer.launch.py file, use the following ROS 2 command:
ros2 launch jarvis_slam cartographer.launch.py exploration:= true/false
Cartographer for Mapping
What is Cartographer?
Cartographer is a highly efficient open-source SLAM solution developed by Google. It can create 2D or 3D maps in real-time and is designed to work with a wide range of sensors, such as LIDAR and IMUs. Cartographer provides accurate and scalable mapping for robots in indoor and outdoor environments.
Features of Cartographer:
- 2D and 3D Mapping: Supports both 2D laser-based SLAM and 3D multi-sensor fusion SLAM.
- Real-time Processing: Capable of performing SLAM in real-time, even in large and complex environments.
- Loop Closure Detection: Automatically detects when the robot revisits a previously mapped location, refining the map.
How Cartographer is Used in JarvisBot:
- LIDAR Integration: JarvisBot’s LIDAR provides distance and obstacle data, which is fed into Cartographer for mapping.
- IMU and Odometry Fusion: Cartographer uses IMU data to estimate the robot's orientation and movement while also utilizing wheel encoders for odometry.
- Pose Graph Optimization: Cartographer builds a pose graph from the sensor data and optimizes it to generate a consistent map, even in large environments.
Benefits for JarvisBot:
- Accurate Mapping: Cartographer’s loop closure and optimization techniques result in highly accurate maps.
- Scalability: Can handle large and dynamic environments, making it ideal for complex navigation tasks.
- Ease of Use: Cartographer is modular and integrates smoothly into ROS, enabling easy deployment on JarvisBot.
Conclusion
JarvisBot leverages the power of SLAM for autonomous navigation, using state-of-the-art algorithms and tools like Cartographer for real-time localization and mapping. These technologies enable JarvisBot to understand and interact with its environment effectively, even in unknown or changing environments.